3.2 Graphical modelling
|
A graphical model is a visualization of an idea, often created on paper or through software.
|
|
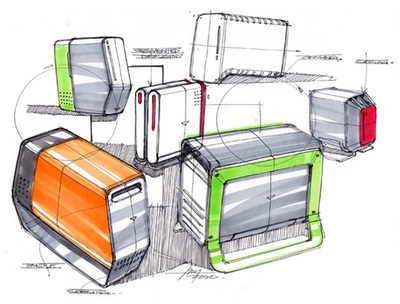
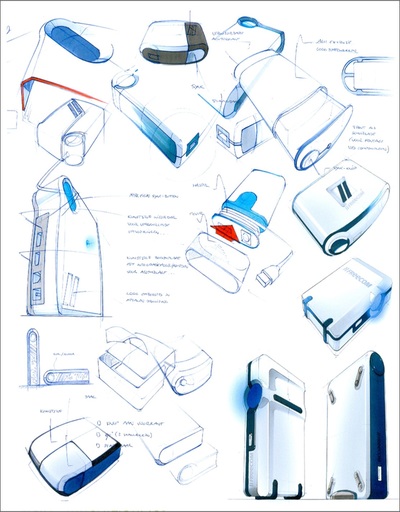
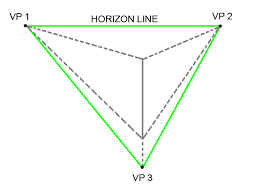
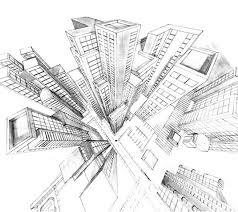
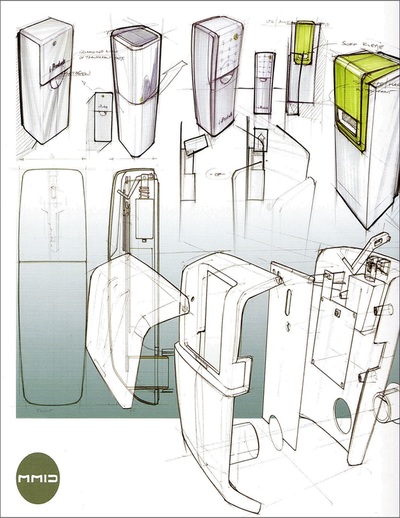
Sketching: Used in the early stages and is quick and easy. 3-D sketches provide designers with a sense of form, proportion and aesthetics, whilst 2-D sketches are able to isolate and detail more features. Good for communication initial design concepts
|
|
|
|
Drawings: These can be done by CAD or by hand. Drawings are more technical and take longer
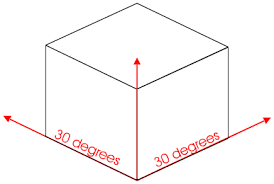
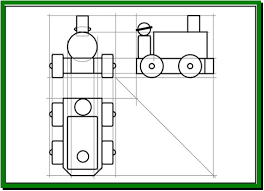
Isometric: An isometric drawing depicts the proposed solution in 3D showing shape and form. They are drawn on a 30/90/30 degree access.
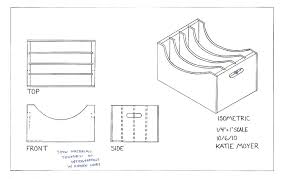
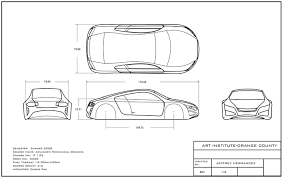
Orthographic: Orthographic projection can be first or third angle. Orthographic projection (or orthogonal projection) is a means of representing a three-dimensional object in two dimensions. These are particularly for the manufacturer and include dimensions.
Orthographic: Orthographic projection can be first or third angle. Orthographic projection (or orthogonal projection) is a means of representing a three-dimensional object in two dimensions. These are particularly for the manufacturer and include dimensions.
|
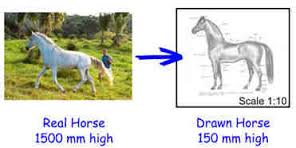
Scale Drawings
A map cannot be of the same size as the area it represents. So, the measurements are scaled down to make the map of a size that can be conveniently used by users such as motorists, cyclists and bushwalkers. A scale drawing of a building (or bridge) has the same shape as the real building (or bridge) that it represents but a different size. Builders use scaled drawings to make buildings and bridges A scale is usually expressed in one of two ways:
|
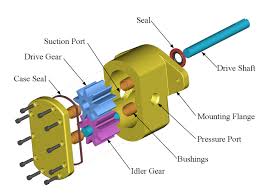
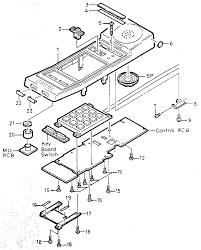
Part drawing or exploded view: These are visually descriptive and used during assembly. An isometric drawing of an object with more than one component that depicts how the parts of assemblies fit together. The drawing is exploded to show component parts of a product and/or the sequence of assembly.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.