8.1 Sustainable development
Designers utilize design approaches that support sustainable development across a variety of contexts. A holistic and systematic approach is needed at all stages of design development to satisfy all stakeholders. In order to develop sustainable products, designers must balance aesthetic, cost, social, cultural, energy, material, health and usability considerations.
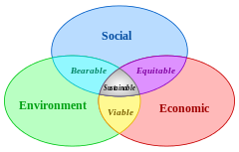
Triple bottom line sustainability does not only focus on the profitability of an organization or product, but also the environmental and social benefit it can bring. Organizations that embrace triple bottom line sustainability can make significant positive effects to the lives of others and the environment by changing the impact of their business activities
Triple bottom line sustainability does not only focus on the profitability of an organization or product, but also the environmental and social benefit it can bring. Organizations that embrace triple bottom line sustainability can make significant positive effects to the lives of others and the environment by changing the impact of their business activities
Sustainability
•is the capacity to endure and maintain.
•Sustainability is the long-term maintenance of responsibility, which has environmental, economic and social dimensions.
•is the capacity to endure and maintain.
•Sustainability is the long-term maintenance of responsibility, which has environmental, economic and social dimensions.
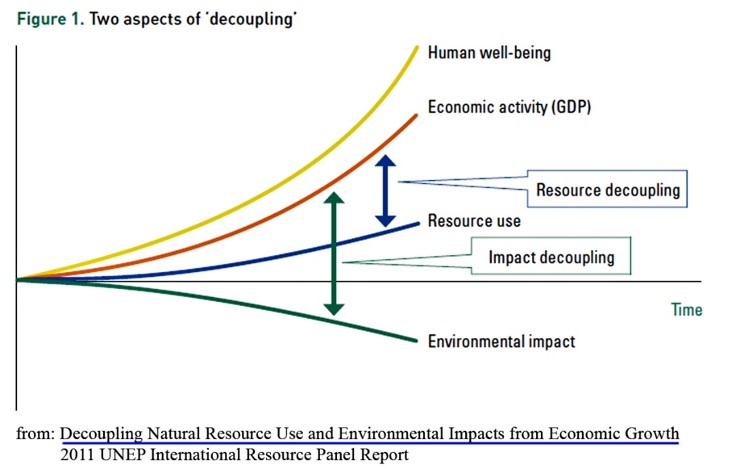
Decoupling
disconnecting economic growth and environmental impact so that one no longer depends on the other.
Consider the benefits and limitations of decoupling as an appropriate strategy for sustainability.
Decoupling refers to disconnecting two trends so that one no longer depends on the other. Through the act of decoupling (using resources more productively and redesigning production systems), it is technically possible to deliver the same or equivalent goods and services with lower environmental impact while maintaining social and equity benefits.
disconnecting economic growth and environmental impact so that one no longer depends on the other.
Consider the benefits and limitations of decoupling as an appropriate strategy for sustainability.
Decoupling refers to disconnecting two trends so that one no longer depends on the other. Through the act of decoupling (using resources more productively and redesigning production systems), it is technically possible to deliver the same or equivalent goods and services with lower environmental impact while maintaining social and equity benefits.
International and national laws
The use of international and national laws to promote sustainable development.
How international and national laws encourage companies to focus on something other than shareholder value and financial performance.
The use of international and national laws to promote sustainable development.
How international and national laws encourage companies to focus on something other than shareholder value and financial performance.
Sustainability reporting
Benefits of sustainability reporting for governments, manufacturers and consumers
Economic
Environmental
Social
Governance
A sustainability report is a company report that focuses on four aspects of performance. The reliability and acceptance of sustainability reporting requires accurate data gathering to be maintained over a lengthy period of time. Students need to be able to explain the benefits of sustainability reporting for
governments,
manufacturers
and consumers.
“A sustainability report is an organizational report that gives information about economic, environmental, social and governance performance”.
“Sustainability reporting is not just report generation from collected data; instead it is a method to internalize and improve an organization’s commitment to sustainable development in a way that can be demonstrated to both internal and external stakeholders”
Benefits of sustainability reporting for governments, manufacturers and consumers
Economic
Environmental
Social
Governance
A sustainability report is a company report that focuses on four aspects of performance. The reliability and acceptance of sustainability reporting requires accurate data gathering to be maintained over a lengthy period of time. Students need to be able to explain the benefits of sustainability reporting for
governments,
manufacturers
and consumers.
“A sustainability report is an organizational report that gives information about economic, environmental, social and governance performance”.
“Sustainability reporting is not just report generation from collected data; instead it is a method to internalize and improve an organization’s commitment to sustainable development in a way that can be demonstrated to both internal and external stakeholders”
|
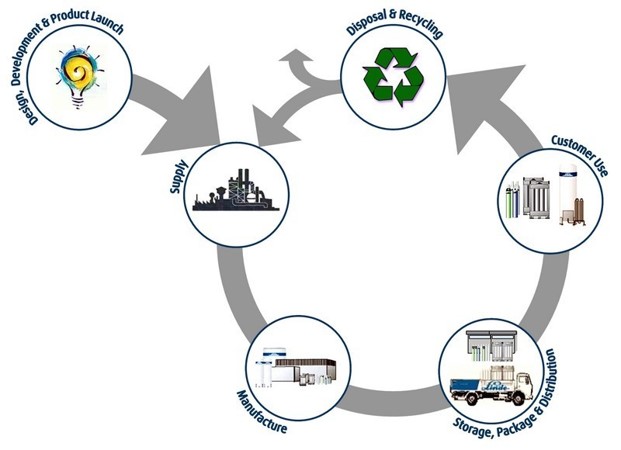
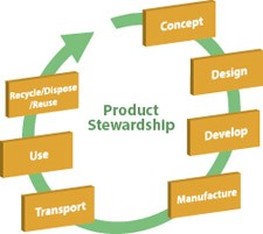
Product stewardship
Product stewardship examples include organic foods, genetically modified food, green cotton, forest stewardship and bio-plastics Designers may need to respond to consumer pressure as more consumers become aware of resource issues and product labelling. Product stewardship requires all stakeholders involved in making, buying, selling or handling equipment to take responsibility for minimizing environmental, health and safety impact at all stages of the life cycle. The following areas should be explored through case studies in terms of product stewardship: organic foods genetically modified food green cotton forest stewardship bioplastics. |