4.2c

Glass is an unlimited and innovative material that has plenty of applications. It is an essential component of numerous products that we use every day, most often without noticing it.
It is clear that modern life would not be possible without glass!
Glass is used in the following non-exhaustive list of products:
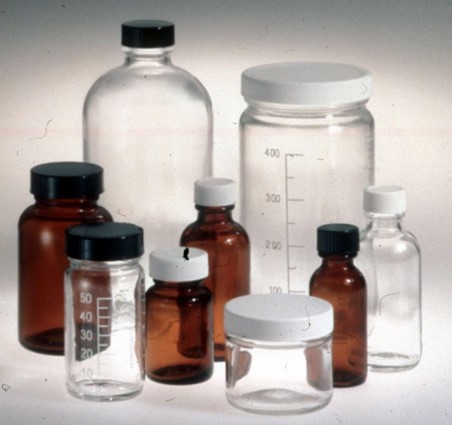
Packaging (jars for food, bottles for drinks, flacon for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals)
Tableware (drinking glasses, plate, cups, bowls)
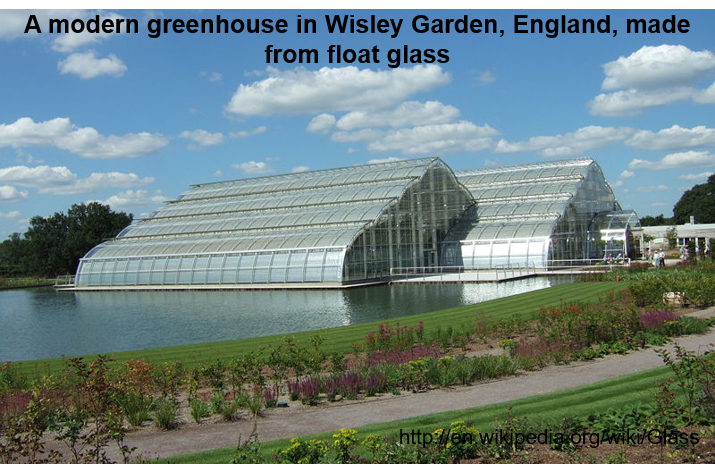
Housing and buildings (windows, facades, conservatory, insulation, reinforcement structures)
Interior design and furnitures (mirrors, partitions, balustrades, tables, shelves, lighting)
Appliances and Electronics (oven doors, cook top, TV, computer screens, smart-phones)
Automotive and transport (windscreens, backlights, light weight but reinforced structural components of cars, aircrafts, ships, etc.)
Medical technology, biotechnology, life science engineering, optical glass
Radiation protection from X-Rays (radiology) and gamma-rays (nuclear)
Fibre optic cables (phones, TV, computer: to carry information)
Renewable energy (solar-energy glass, windturbines)
All of this is made possible by the countless properties of the glass substance.
It is clear that modern life would not be possible without glass!
Glass is used in the following non-exhaustive list of products:
Packaging (jars for food, bottles for drinks, flacon for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals)
Tableware (drinking glasses, plate, cups, bowls)
Housing and buildings (windows, facades, conservatory, insulation, reinforcement structures)
Interior design and furnitures (mirrors, partitions, balustrades, tables, shelves, lighting)
Appliances and Electronics (oven doors, cook top, TV, computer screens, smart-phones)
Automotive and transport (windscreens, backlights, light weight but reinforced structural components of cars, aircrafts, ships, etc.)
Medical technology, biotechnology, life science engineering, optical glass
Radiation protection from X-Rays (radiology) and gamma-rays (nuclear)
Fibre optic cables (phones, TV, computer: to carry information)
Renewable energy (solar-energy glass, windturbines)
All of this is made possible by the countless properties of the glass substance.
Glass is composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) together with some sodium oxide (Na2O) and calcium oxide (CaO) and small quantities of a few other chemicals (generally metal oxides).
Glass is an amorphous substance (a solid that is not crystalline) made primarily of silica fused at high temperatures with borates or phosphates. Glass is also found in nature, as the volcanic material obsidian and making the enigmatic objects known as tektites.
Glass is called amorphous because it is neither a solid nor a liquid but exists in a vitreous, or glassy, state in which molecular units have disordered arrangement but sufficient cohesion to produce mechanical rigidity. Glass is cooled to a rigid state without the occurrence of crystallisation; heating can reconvert glass to a liquid form.
Usually transparent, glass can also be translucent or opaque. Colour varies with the ingredients of the batch from which the glass is made.
The basic ingredient of glass – silica (silicon dioxide) derived from sand, flint, or quartz. Calcium carbonate (limestone) is the source of calcium dioxide and sodium oxide is taken from sodium carbonate (washing soda).
Glass is an amorphous substance (a solid that is not crystalline) made primarily of silica fused at high temperatures with borates or phosphates. Glass is also found in nature, as the volcanic material obsidian and making the enigmatic objects known as tektites.
Glass is called amorphous because it is neither a solid nor a liquid but exists in a vitreous, or glassy, state in which molecular units have disordered arrangement but sufficient cohesion to produce mechanical rigidity. Glass is cooled to a rigid state without the occurrence of crystallisation; heating can reconvert glass to a liquid form.
Usually transparent, glass can also be translucent or opaque. Colour varies with the ingredients of the batch from which the glass is made.
The basic ingredient of glass – silica (silicon dioxide) derived from sand, flint, or quartz. Calcium carbonate (limestone) is the source of calcium dioxide and sodium oxide is taken from sodium carbonate (washing soda).

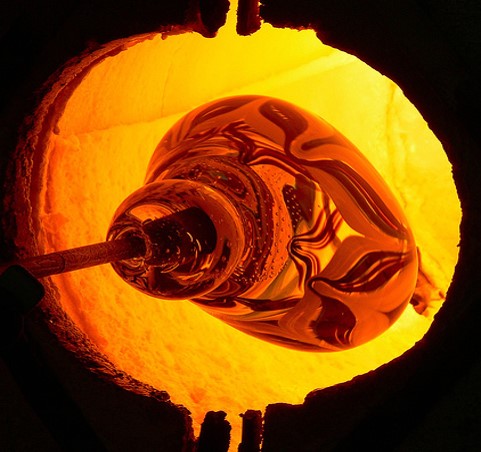
The production of glass requires large amounts of energy due to the high melting point of the raw materials and the strength of the chemical (ionic) bonds involved. Silicon dioxide SiO2 has a melting point of 2000 K.
To make the production of glass cheaper scrap glass is added to new raw materials. By adding up to between 15-30% powdered glass the amount of energy (in the form of electricity) and time required to produce usable glass can be greatly reduced.
|
From Silica To Cullet
Powdered glass cullet is made from ground recycled glass, which begins life as virgin glass, a product made primarily from silica sand with certain additives combined with it to lower the melting point and increase chemical resistance. There are a variety of types of glass available on the market, but the most common glass in circulation today, and the type most often found in glass cullet form, is soda-lime glass. This type of glass contains between 70 to 74 percent silica, and is the glass from which most all bottles and jars are made. http://www.glasscullet.com/powdered-glass-cullet/ |
Glass is a hard material normally fragile and transparent common in our daily life. It is composed mainly of sand (silicates, SiO2) and an alkali.
These materials at high temperature (i.e. molten viscous state) fuse together; then they are cooled rapidly forming a rigid structure, however not having enough time to form a crystalline regular structure.
These materials at high temperature (i.e. molten viscous state) fuse together; then they are cooled rapidly forming a rigid structure, however not having enough time to form a crystalline regular structure.

Main properties of glass (from Lenntech)
These are the main characteristics of glass:
These are the main characteristics of glass:
- Solid and hard material
- Disordered and amorphous structure
- Fragile and easily breakable into sharp pieces
- Transparent to visible light
- Inert and biologically inactive material.
- Glass is 100% recyclable and one of the safest packaging materials due to its composition and properties
IB Characteristics of glass
- Glass is brittle, Glass is brittle because it does not have good large-area orderly crystalline structure. If it did, it would be like sheet metal steel, where it dents and deforms instead of shattering.
- Glass is usually transparent, glass can also be translucent or opaque. Colour varies with the ingredients of the batch from which the glass is made.
- Glass is hard, glass is resistant to scratching.
- Glass is unreactive Glass does not deteriorate, corrode, stain or fade and therefore is one of the safest packaging materials.
- Glass is an aesthetically pleasing material an is used in architecture, as a decoration and in jewellery.
Commercial glass or Soda-lime glass:
This is the most common commercial glass and lest expensive. The composition of soda-lime glass is normally 60-75% silica, 12-18% soda, and 5-12% lime. A low percentage of other materials can be added for specific properties such as colouring.
This is the most common commercial glass and lest expensive. The composition of soda-lime glass is normally 60-75% silica, 12-18% soda, and 5-12% lime. A low percentage of other materials can be added for specific properties such as colouring.
- It has light transmission appropriate to be use in flat glass in windows;
- It has a smooth and nonporous surface that allows glass bottles and packaging glass to be easily cleaned;
- Soda-lime glass containers are virtually inert, resistant to chemical attack from aqueous solutions so they will not contaminate the contents inside or affect the taste.
Whereas pure glass SiO2 does not absorb UV light, soda-lime glass does not allow light at a wavelength of lower than 400 nm (UV light) to pass.
The disadvantages of soda-lime glass is that is not resistant to high temperatures and sudden thermal changes. For example, everybody has experienced a glass breaking down when pouring liquid at high temperature, for example to make tea.
Some of the use of soda-lime glass is primarily used for bottles, jars, everyday drinking glasses, and window glass.
http://www.lenntech.com/Glass.htm
The disadvantages of soda-lime glass is that is not resistant to high temperatures and sudden thermal changes. For example, everybody has experienced a glass breaking down when pouring liquid at high temperature, for example to make tea.
Some of the use of soda-lime glass is primarily used for bottles, jars, everyday drinking glasses, and window glass.
http://www.lenntech.com/Glass.htm
Pyrex is a brand name for glassware, introduced by Corning Incorporated in 1915. Originally, Pyrex was made from thermal shock resistant borosilicate glass.

Borosilicate glass:
Borosilicate glass is mainly composed of silica (70-80%), boric oxide B2O3 (7-13%) and smaller amounts of the alkalis (sodium and potassium oxides) such as 4-8% of Na2O and K2O, and 2-7% aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
Boron gives greater resistance to thermal changes and chemical corrosion.
It is suitable for industrial chemical process plants, in laboratories, in the pharmaceutical industry, in bulbs for high-powered lamps, etc. Borosilicate glass is also used in the home for cooking plates and other heat-resistant products. It is used for domestic kitchens and chemistry laboratories, this is because it has greater resistance to thermal shock and allows for greater accuracy in laboratory measurements when heating and cooling experiments.
http://www.lenntech.com/Glass.htm
Borosilicate glass is mainly composed of silica (70-80%), boric oxide B2O3 (7-13%) and smaller amounts of the alkalis (sodium and potassium oxides) such as 4-8% of Na2O and K2O, and 2-7% aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
Boron gives greater resistance to thermal changes and chemical corrosion.
It is suitable for industrial chemical process plants, in laboratories, in the pharmaceutical industry, in bulbs for high-powered lamps, etc. Borosilicate glass is also used in the home for cooking plates and other heat-resistant products. It is used for domestic kitchens and chemistry laboratories, this is because it has greater resistance to thermal shock and allows for greater accuracy in laboratory measurements when heating and cooling experiments.
http://www.lenntech.com/Glass.htm
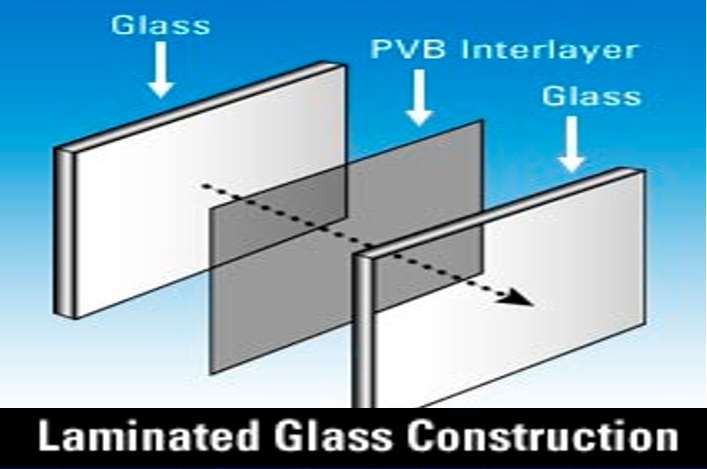
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass that holds together when shattered. In the event of breaking, it is held in place by an , typically of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), between its two or more layers of glass. The interlayer keeps the layers of glass bonded even when broken, and its high strength prevents the glass from breaking up into large sharp pieces. This produces a characteristic "spider web" cracking pattern when the impact is not enough to completely pierce the glass.
Tempered or Toughened Safety Glass
The "heat-treatment" process of tempered glass provides safety characteristics giving it additional strength, resistance to thermal stress and impact resistance. Additionally, when fully tempered glass breaks it fractures into small, relatively harmless fragments. And markedly reduces the likelihood of injury to people as there are no jagged edges or sharp shards.
The "heat-treatment" process of tempered glass provides safety characteristics giving it additional strength, resistance to thermal stress and impact resistance. Additionally, when fully tempered glass breaks it fractures into small, relatively harmless fragments. And markedly reduces the likelihood of injury to people as there are no jagged edges or sharp shards.

Laminated Glass is made up of a vinyl laminate (PVB) layer bonded together between two panes of glass under heat and pressure. Laminated glass may crack upon impact, however the glass fragments typically stick to the protective inter-layer rather than falling free and potentially causing injury. It breaks exactly like the windshield of your car, cracks but is held in place by the vinyl laminate layer.
The ultraviolet filtering performance of the protective inter-layer helps protect valuable furnishings, displays or merchandise from the fading effects of the sun's UV light.
The ultraviolet filtering performance of the protective inter-layer helps protect valuable furnishings, displays or merchandise from the fading effects of the sun's UV light.
|
Flat glass, sheet glass, or plate glass is a type of glass, initially produced in plane form, commonly used for windows, glass doors, transparent walls, and windshields. For modern architectural and automotive applications, the flat glass is sometimes bent after production of the plane sheet. Most flat glass is soda-lime glass, produced by the float glass process. Impressive castle-like spires crown internationally acclaimed PPG Place, with locally produced mirror-glass panels covering the intricate structure. Headquarters of PPG Industries, formerly Pittsburgh Plate Glass Company, the three-city-block complex includes five silver glass buildings surrounding a 60-story glass tower. Designed by architect Philip Johnson as part of Pittsburgh's second renaissance. |

Glass Blocks in a Domestic Environment
Glass Blocks are available in a range of styles, colours and properties. This gives them the versatility to be used almost anywhere in the home and even in the garden.
Glass Blocks provide:
http://www.buildingdesign.co.uk/facil-group2/new-age-glass/
Glass Blocks are a non-load bearing material. Provisions (i.e.lintels) at the head should be provided to accommodate the support of loads above the glass block panel (similar to doors and windows).
http://www.pittsburghcorning.com/homeowners/faq1.asp
Glass Blocks are available in a range of styles, colours and properties. This gives them the versatility to be used almost anywhere in the home and even in the garden.
Glass Blocks provide:
- Excellent heat insulation
- Sound insulation
- Varying degrees of privacy
- Natural light
- Atmosphere to any room or setting
http://www.buildingdesign.co.uk/facil-group2/new-age-glass/
Glass Blocks are a non-load bearing material. Provisions (i.e.lintels) at the head should be provided to accommodate the support of loads above the glass block panel (similar to doors and windows).
http://www.pittsburghcorning.com/homeowners/faq1.asp
21st Century Glass
bioglass for bone replacement therapy
– glass is dissolved and replaced with bone
– composition and pores stimulate cells
solar energy
– transparent protective layer for solar cells
– need to find glass that weighs less
Sustainability & the Environment
Glass is a sustainable, fully recyclable material which provides great environmental benefits such as contributing to mitigating climate change and saving precious natural resources. It is also highly appreciated in many applications for its inert nature and its contributions to safeguarding people’s health ad well being.
Mitigate climate change
In many of its application glass can help to save energy. It is most obvious in the case for insulating glass for windows and facades but also for less known products such as weight-lightening reinforcement glass fibre used in automotive, aviation and other transport modes to reduce the weight of vehicle and their fuel consumption.
Glass is also used to generate renewable energy through solar-thermal and photovoltaic applications and wind turbine, which largely profit from light weight reinforcement glass fibres.
bioglass for bone replacement therapy
– glass is dissolved and replaced with bone
– composition and pores stimulate cells
solar energy
– transparent protective layer for solar cells
– need to find glass that weighs less
Sustainability & the Environment
Glass is a sustainable, fully recyclable material which provides great environmental benefits such as contributing to mitigating climate change and saving precious natural resources. It is also highly appreciated in many applications for its inert nature and its contributions to safeguarding people’s health ad well being.
Mitigate climate change
In many of its application glass can help to save energy. It is most obvious in the case for insulating glass for windows and facades but also for less known products such as weight-lightening reinforcement glass fibre used in automotive, aviation and other transport modes to reduce the weight of vehicle and their fuel consumption.
Glass is also used to generate renewable energy through solar-thermal and photovoltaic applications and wind turbine, which largely profit from light weight reinforcement glass fibres.
Save natural resources
Glass is a resource efficient material which is made of abundant natural raw material such as sand and glass waste (cullets). Glass is a fully recyclable material that can be recycled in close loop over and over again.
This is particularly true for glass bottles which on average have a recycling rate varying from 50% to 80%. Thanks to glass recycling, significant amounts of raw materials are saved and natural resources are preserved. Glass recycling also helps in saving energy as cullets melt at a lower temperature than raw materials. Consequently, less energy is required for the melting process.
In other glass sectors, considerable efforts are made to recycle glass after use even though each sector has its own specificities and quality requirements. The amount of solid waste produced by the glass industries during manufacturing is extremely low in the glass industries as almost all glass waste (cullets) are immediately recycled and put back to furnaces to serve as raw material.
Safeguard people’s health and well-being
Glass is among the preferred materials not only for its aesthetics but also for its own characteristics. Glass preserves taste and vitamins. As an inert material, it guarantees that food and beverages placed in glass containers are not stained by the packaging. It is also commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to preserve the properties of medicines. In another side of the medical sector, optical glass helps improve the vision of millions of Europeans.
In construction as well, architects not only use large glazed areas for their energy-saving properties but also because they provide natural light into buildings which enhance living and working conditions of occupants. Studies show that glass in buildings, through all these benefits, contribute to people’s well-being and improved health conditions.
Glass is a resource efficient material which is made of abundant natural raw material such as sand and glass waste (cullets). Glass is a fully recyclable material that can be recycled in close loop over and over again.
This is particularly true for glass bottles which on average have a recycling rate varying from 50% to 80%. Thanks to glass recycling, significant amounts of raw materials are saved and natural resources are preserved. Glass recycling also helps in saving energy as cullets melt at a lower temperature than raw materials. Consequently, less energy is required for the melting process.
In other glass sectors, considerable efforts are made to recycle glass after use even though each sector has its own specificities and quality requirements. The amount of solid waste produced by the glass industries during manufacturing is extremely low in the glass industries as almost all glass waste (cullets) are immediately recycled and put back to furnaces to serve as raw material.
Safeguard people’s health and well-being
Glass is among the preferred materials not only for its aesthetics but also for its own characteristics. Glass preserves taste and vitamins. As an inert material, it guarantees that food and beverages placed in glass containers are not stained by the packaging. It is also commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to preserve the properties of medicines. In another side of the medical sector, optical glass helps improve the vision of millions of Europeans.
In construction as well, architects not only use large glazed areas for their energy-saving properties but also because they provide natural light into buildings which enhance living and working conditions of occupants. Studies show that glass in buildings, through all these benefits, contribute to people’s well-being and improved health conditions.